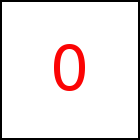
resizeZ Library Method
Short Description: Resize to compensate Distance
Signature: t.resizeZ ([z0,[z1,[z0_dest,[z1_dest]]]])
Group: Light and Shadow
Class: transition Class
Unfortunately this method is quite difficult to describe,
although it performs quite a simple function. So we start
with an example and a simplified (but incomplete) explanation
(that is nevertheless sufficient for many applications) and
give a more precise description later:
Simplified Description
If resizeZ is called without parameters or with the z-coordinate of
the current transition as parameter,
then it makes sure that the animated element is not resized.
Normally in 3D mode, an element that is moved towards the eye,
i.e. towards negative z-coordinates, becomes larger.
The perspective of taccgl™ normally is adjusted so that an HTML element
displayed at z=0 is not resized, while it is enlarged for z<0
and becomes smaller for z>0.
The following examples demonstrate that. The second example produces
the same output as the first one and the third example is just for
comparision how it looks without resizeZ.
taccgl.a(document.body).shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); taccgl.actor("ex1").position(100,500,-1000).resizeZ().dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a(document.body).shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); taccgl.actor("ex1").position(100,500,-1000).resizeZ(-1000).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a(document.body).shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); taccgl.actor("ex1").position(100,500,-1000).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
It is often required to display elements at non-zero z-coordinates to get shadows
looking nice, see posZ and Shadows in 3D HTML Pages.
Then resizeZ is useful to avoid resizing.
If the element undergoes an animation using e.g. from or to
which animates the z-coordinate, then no resizing takes place at the start
of the animation. While the animation is playing the element grows or shrinks
if the element moved towards or away from the viewer.
If the argument z0 is the string "out", then no resizing takes
place at the end of the animation. If the argument z0 is the string "both", then
no resizing takes place at the begin and the end of the animation.
Complete Description
The 3D engine itself does not know a thing like "not resizing", which is
just incorrect from a perspective point of view.
So in order to "not resize" an element resizeZ actually resizes
the animated element in 3D space in a way that compensates for the later
occurring perspective growing or shrinking:
resizeZ resizes the element or object drawn with the transition,
just like resize. However, instead of getting the
new size as parameter (as resize), resizeZ gets
(in its one-argument form) a z-coordinate z0 as parameter.
The element or object is resized in the 3D space, so that if it is or was displayed at
z-coordinate z0 actually no resizing in the 2D space occurs.
In other words it grows the element so that the perspective growing of the element
that occurs when displayed at z-coordinate z0 is undone.
The z-coordinate z0 passed to resizeZ does not neccesarily
need to be identical to the z-position of the element. resizeZ
just performs a resize in 3D space, whereby the resizing factor is
controlled by z0, the resize itself, however is independent
of the position of the element.
The argument z0 defaults to the z-coordinate of the transition.
If it is a motion animation then it defaults to the z-coordinate of the starting point of
the animation. If the string "out" is passed as parameter z0 then
the z-coordinate of the end point of the animation is taken as value for z0.
taccgl.actor("ex2").from(0,1000,3000).to(300,1000,-1000).resizeZ(-1000).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a("Middle").shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); taccgl.actor("ex2").from(0,1000,3000).to(0,1000,-1000).resizeZ(-1000).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a("Middle").shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); taccgl.actor("ex2").from(0,1000,3000).to(0,1000,-1000).resizeZ("out").dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a("Middle").shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); taccgl.actor("ex2").from(0,1000,3000).to(0,1000,-1000).resizeZ(3000).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a("Middle").shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); taccgl.actor("ex2").from(0,1000,3000).to(0,1000,-1000).resizeZ().dur(5).start(); | RUN |
z1
By specifying z1 a grow or shrink animation can be performed.
z0 gives the resize factor at the begin of the animation, and z1
at the end of the animation. Both factors are given in the form of z-coordinates as
discussed above.
If the string "both" is passed as z0 parameter and the transition
has a motion animation, then for z0 the z-coordinate of the starting
point of the animation is taken and for z1 the z-coordinate of the end point.
taccgl.actor("ex2").resizeZ(0,-1000).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.actor("ex2").resizeZ(0,1000).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a(document.body).shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); a=taccgl.actor("ex2"); a.to(a.x,a.y,-1500).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a(document.body).shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); a=taccgl.actor("ex2"); a.to(a.x,a.y,-1500).resizeZ(0,-1500).dur(5).start(); | RUN |
taccgl.a(document.body).shadowOnly().color("black").showAfter().start(); a=taccgl.actor("ex2"); a.to(a.x,a.y,-1500).resizeZ("both").dur(5).start(); | RUN |
As demonstrated by the last example above, this kind of resizing animation can
be used to compensate for the perspective growing of an element that flies
towards the viewer. This is a quite unnatural animation which
however might be useful to attach a label or name tag to a 3D object,
whereby the label or name tag does not change in size because it is not
really part of the scene.
z0_dest and z1_dest
resizeZ resizes the associated element or object
(just as resize). The scale factor of the resize operation
is given using the z0 and z0_dest parameters.
Normally (the image) of an object grows or shrinks when moved
towards or away from the eye. The scale factor is determined
by virtually moving the element or object from z-coordinate
z0 to z0_dest and finding out
by what factor the image would grow or shrink.
If z1 to z1_dest are different from
z0 to z0_dest then a grow or shrink animation
is performed. The inital scale factor is determined as described
from z0 and z0_dest and the final scale factor
using z1 and z1_dest.
Default values for z0_dest and z1_dest are 0,
for z1 the default is z0 and for z0
it is the (initial) z-coordinate of the transition.
WebGL™ is a trademark of the Khronos Group Inc.
|